Introduction
SEO has moved far beyond keyword density and link counts. Today, search engines use artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP) to read context and intent, not just individual words. That shift gave rise to Semantic SEO : a more thoughtful, people-first way to earn visibility.
In this piece we’ll outline the difference between traditional SEO and semantic SEO , show how each approach operates, and explain why search is now about understanding meaning as much as matching phrases.
Understanding the Basics of SEO
At its simplest, SEO (Search Engine Optimization) helps your site appear when people look for topics, products, or services online. It means structuring and writing content so search engines can crawl, index, and rank your pages accurately.
Over the years SEO has shifted from a keyword-first tactic to a context-first discipline — a change driven by semantic understanding and machine learning.
What Is Traditional SEO?
Before AI began interpreting nuance, SEO was mostly mechanical. Traditional SEO prioritized exact keyword matches — if your page used the same terms a user searched for, it stood a better chance of ranking.
Core Principles of Traditional SEO
- Keyword Optimization: Targeting exact-match phrases in titles, headings, and body text.
- Meta Tags: Writing title tags and meta descriptions around target keywords.
- Backlink Building: Earning external links to signal authority.
- On-Page Optimization: Improving load speed, image alt text, and mobile experience.
Strengths and Limitations of Traditional SEO
Advantages:
- Simple to plan and track.
- Effective for narrow, stable niches.
- Helps get pages indexed and discovered quickly.
Limitations:
- Overuse of keywords can lead to keyword stuffing .
- Often misses the true user intent behind queries.
- Struggles with voice search and conversational queries.
Think of traditional SEO as following a map — neat and structured, but inflexible. As Google grew smarter, that map evolved into a responsive GPS , and Semantic SEO became necessary.
What Is Semantic SEO?
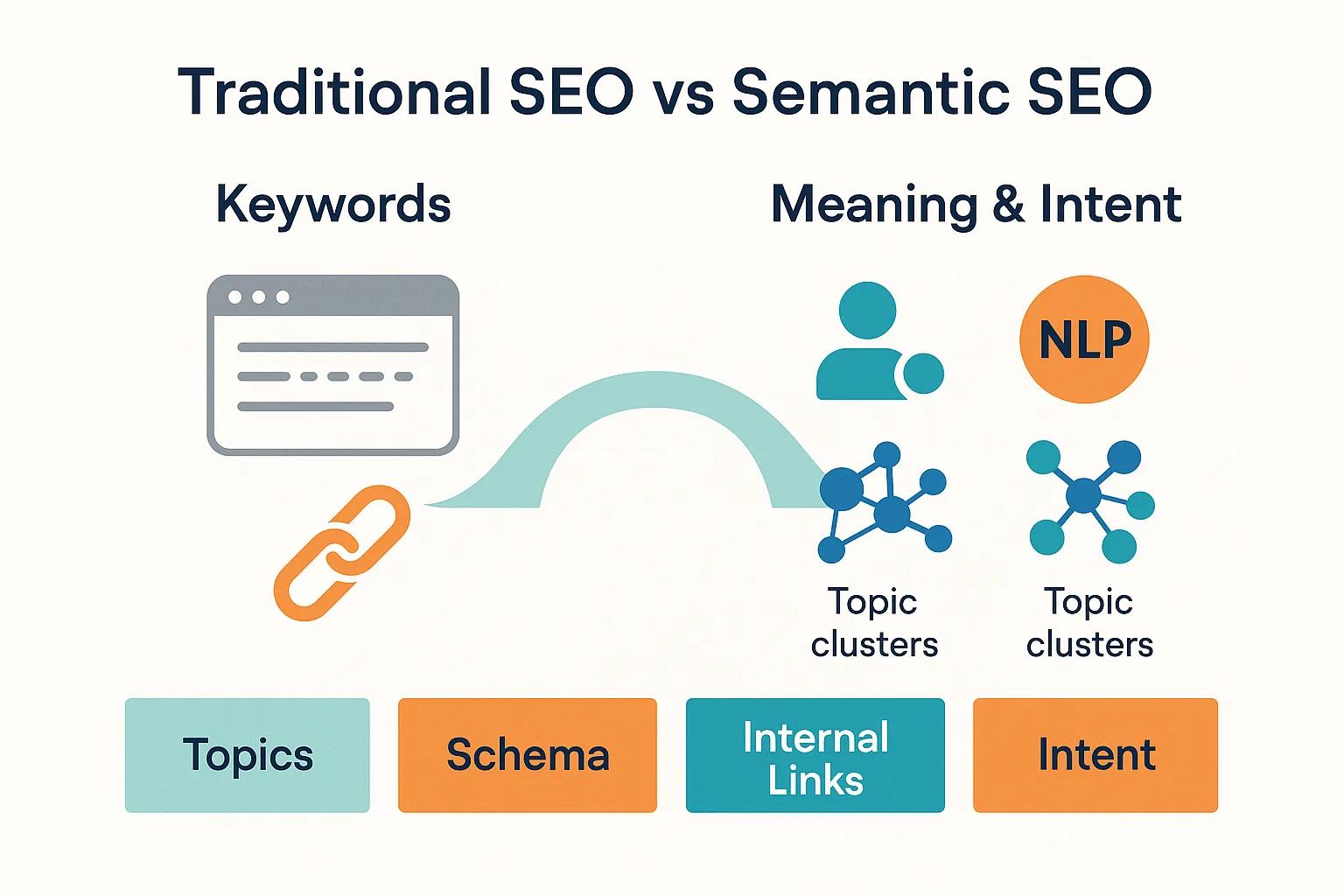
Semantic SEO moves past individual keywords to emphasize meaning , context , and the relationships between ideas. It’s about helping search engines understand what users really want , not just the words they enter. Learn more about master SEO link building techniques today .
For example, a search for “best running shoes for flat feet” should return content addressing comfort, arch support , and suitable brands — even if the exact phrase isn’t repeated verbatim.
How Semantic SEO Works
- Entities and Concepts: Search engines map people, places, products, and their connections.
- NLP and AI: Models like BERT and MUM interpret nuance and relationships in language.
- Contextual Relevance: Pages rank based on how well they satisfy the user’s underlying question, not just keyword overlap.
Key Elements of Semantic SEO
- Schema Markup: Structured data that clarifies entities and attributes for search engines.
- Topic Clusters: Pillar pages with logically connected subtopics that signal expertise.
- Search Intent Optimization: Writing to resolve informational, navigational, or transactional needs.
- E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness): Proof that your content is credible and useful.
Traditional SEO vs Semantic SEO — The Core Differences
| Aspect | Traditional SEO | Semantic SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Keywords | Context & meaning |
| Goal | Match search terms | Answer user intent |
| Optimization | On-page elements | Entity and topic relationships |
| Algorithm Basis | Keyword signals | Machine learning and NLP |
| Content Type | Standalone articles | Interconnected topic clusters |
| Example Query Handling | Literal interpretation | Contextual understanding |
Semantic SEO doesn’t discard traditional tactics — it refines and complements them. Traditional tactics
Why Semantic SEO Is the Future of Search Optimization
With AI-driven systems like RankBrain , BERT , and MUM , Google reads language more like a person. That shifts the emphasis from how often a keyword appears to how well your content answers the question behind it.
Brands that adopt semantic SEO typically see: seo tools
- Higher visibility for long-tail and conversational queries.
- Better chances of appearing in featured snippets and People Also Ask .
- Stronger user engagement and improved on-site metrics.
Implementing Semantic SEO in Your Strategy
Practical steps to move from traditional to semantic SEO :
- Focus on Topics, Not Keywords: Build comprehensive clusters around central themes.
- Use Schema Markup: Make entities and relationships explicit for search engines.
- Analyze Search Intent: Match content to informational, navigational, or transactional needs.
- Create Internal Links: Connect related pages to show topical depth.
- Leverage Tools: Use platforms like SurferSEO , Frase , or MarketMuse to guide semantic optimization.
Common Myths About Semantic SEO
- “Keywords Don’t Matter Anymore.” Not true — keywords remain useful, but relevance and context carry more weight.
- “It’s Only for Advanced SEOs.” Anyone can apply semantic principles; start with clear topic structure and intent-focused content.
- “Semantic SEO Replaces Backlinks.” No — backlinks still signal authority; semantic SEO improves content quality around those signals.
- “It’s Just About Schema Markup.” Schema helps, but it’s only one part of a broader strategy.
FAQs About The Difference Between Traditional SEO and Semantic SEO
Q1: What is the main difference between traditional SEO and semantic SEO? Traditional SEO targets keywords; semantic SEO targets meaning and intent.
Q2: Does semantic SEO replace traditional SEO? No — it builds on traditional practices, adding context and topical depth.
Q3: How do I apply semantic SEO to my blog? Create topic clusters, add schema where relevant, and write with clear user intent in mind. master seo link building techniques today .
Q4: Is semantic SEO important for voice search? Yes — voice queries are conversational, so context and intent matter more than exact phrasing. Semantic SEO techniques are important for optimizing content for voice search.
Q5: What tools support semantic SEO? Tools such as MarketMuse , Frase , and SurferSEO can help map topics and optimize content. For more insights, check out SEO tools .
Q6: How does Google’s AI affect semantic SEO? AI models like BERT and MUM let Google better infer intent and surface content that answers real questions .
Conclusion
The difference between traditional SEO and semantic SEO marks a shift in how search engines — and users — find and evaluate content. While traditional SEO prioritized keywords , semantic SEO prioritizes meaning and intent , helping your content connect with real user needs.
If you want sustainable visibility, adopting semantic SEO practices is no longer optional — it’s essential .
External Resource: For a deeper dive, check out Google’s Search Central Documentation on Structured Data.
📧 Stay Updated
Get the latest web development tips and insights delivered to your inbox.