Introduction to Semantic SEO
What Is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is the process of optimizing web content for meaning and context, not just keywords. Unlike traditional SEO, which focused mainly on exact keyword matches, semantic SEO prioritizes understanding the relationships between words, entities, and user intent. This shift allows search engines to interpret what users mean —not just what they type —leading to more accurate and relevant results .
Evolution of Search Engine Optimization
The evolution of SEO has moved from simple keyword-based algorithms to AI-driven systems that understand language like humans. In the early days of SEO, search engines relied on keyword frequency and backlinks . But as users began asking more complex, conversational questions, algorithms needed to evolve. Enter semantic search —a smarter, intent-driven approach.
Why Traditional SEO Needed an Upgrade
Traditional SEO often resulted in keyword-stuffed content that failed to satisfy user intent. Search engines realized that delivering meaningful answers was key to improving user experience. Thus, semantic SEO emerged to focus on concepts, context, and content depth rather than just keyword density.
The Role of Search Engines in Understanding Context
How Search Engines Interpret Meaning Beyond Keywords
Modern search engines use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to interpret the meaning behind search queries. They analyze context, synonyms, and relationships between entities to deliver more relevant results. For example, when a user searches for “apple,” the search engine determines whether they mean the fruit or the tech company based on context .
The Power of Entities, Relationships, and Context
Entities—people, places, or things—are central to semantic search. Search engines map entities and their relationships to understand how concepts connect. This creates a “web of meaning” that enhances accuracy and relevance in search results .
Google's Shift: From Keywords to Intent
Major Google algorithm updates like Hummingbird , RankBrain , and BERT revolutionized how content is processed.
- Hummingbird (2013): Focused on conversational queries.
- RankBrain (2015): Introduced machine learning to interpret unknown queries.
- BERT (2019): Enabled understanding of context and nuance in language.
These advancements allowed Google to prioritize intent over keyword frequency—improving the quality of every search .
How Semantic SEO Enhances User Experience
Delivering Relevant and Intent-Focused Results
Semantic SEO ensures users find what they’re looking for faster. By analyzing intent—informational, navigational, or transactional—search engines serve the most fitting results. This alignment boosts satisfaction and trust. SEO prompts for better rankings .
Reducing Bounce Rates and Improving Engagement
When users land on content that directly answers their queries, they stay longer. This reduces bounce rates, increases dwell time, and signals to search engines that the content is valuable .
Personalization and Contextual Relevance
Semantic SEO also powers personalization. Search engines consider location, search history, and device type to deliver contextually relevant answers. A search for “best coffee shops” yields local results that align with the user’s current intent and situation.
Core Components of Semantic SEO
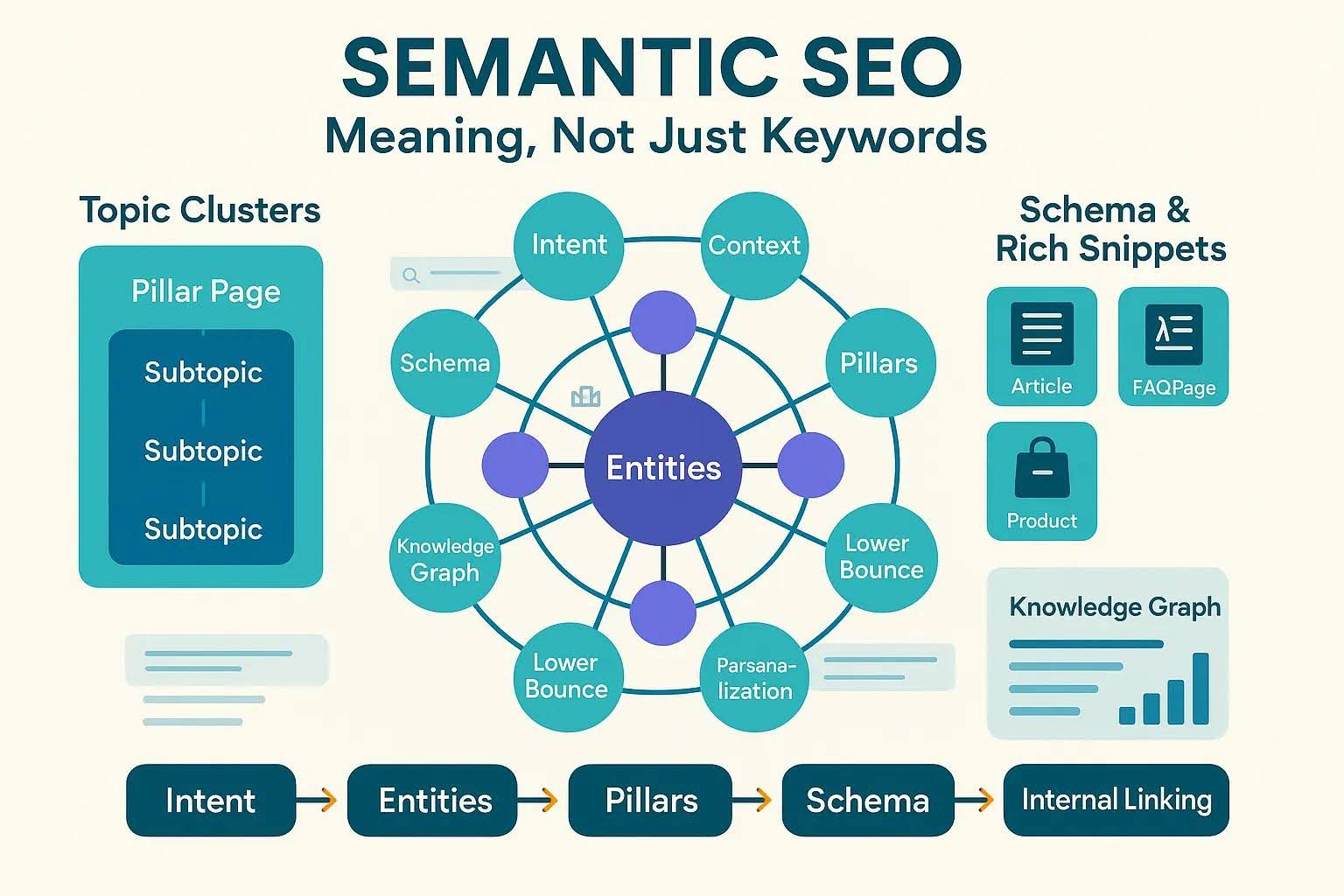
Topic Clusters and Content Pillars
Instead of focusing on single keywords, semantic SEO promotes topic clusters —a central pillar page supported by related subtopics. This approach builds topic authority and strengthens internal linking .
Structured Data and Schema Markup
Schema markup helps search engines understand content meaning. Implementing structured data can enhance search visibility with rich snippets , FAQ boxes , and featured snippets .
Internal Linking and Semantic Relationships
Thoughtful internal linking helps connect related pages, reinforcing topical relevance and helping search engines crawl and understand your content structure .
How Search Engines Apply Semantic Understanding
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning
Search engines use NLP models to interpret sentence structure, synonyms, and sentiment. This enables them to recognize how words relate and predict user intent accurately.
Entity Recognition and Knowledge Graph Integration
The Google Knowledge Graph connects entities and their attributes, displaying relevant data panels directly on the SERP. This enhances UX by providing immediate, credible answers .
Voice Search and Conversational Queries
As voice search grows, semantic understanding becomes even more vital. Voice queries are longer and conversational, requiring engines to grasp context and meaning beyond keywords.
Benefits of Semantic SEO for Users and Websites
Faster Information Retrieval
Semantic SEO allows search engines to fetch answers more efficiently by understanding the meaning behind queries. Instead of matching exact keywords, they can interpret the intent —delivering faster, more precise results. For example, Google can answer, “Who is the CEO of Tesla?” instantly because it recognizes “Elon Musk” as a linked entity in its knowledge graph.
Improved Accuracy of Search Results
Users benefit from highly relevant search results. When semantic signals are optimized, search engines can distinguish between ambiguous terms. Searching “how to plant a seed” won’t yield results about startup funding—it focuses on gardening because the context clarifies the meaning.
Enhanced SERP Features and Rich Snippets
By integrating structured data and schema markup , content can appear in rich results such as featured snippets, carousels, and FAQs. These visual enhancements not only improve visibility but also provide immediate, actionable answers , dramatically improving user experience.
Strategies to Optimize Content for Semantic SEO
Writing for Search Intent Instead of Keywords
Semantic SEO rewards content written for human readers. Focus on addressing the intent behind queries:
- Informational intent: How-to guides and educational content.
- Navigational intent: Brand or site-specific content.
- Transactional intent: Product comparisons or purchase-oriented articles.
By aligning with search intent, your content naturally ranks higher and provides value. better rankings
Using Related and LSI Keywords Naturally
Incorporate Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords —related terms that add context. For instance, if your topic is “semantic SEO,” relevant LSI terms include “entity-based search,” “contextual optimization,” and “search intent.” These keywords help search engines fully understand your content theme .
Implementing Schema and Structured Data Correctly
Adding schema markup (e.g., Article, FAQPage, or Product) provides search engines with structured context about your page. This leads to richer SERP displays and a higher likelihood of earning featured snippets.
👉 Pro Tip: Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to validate your markup.
Real-World Examples of Semantic SEO in Action
How Google’s Knowledge Graph Revolutionized Search
Google’s Knowledge Graph , launched in 2012, transformed how information is connected. Instead of displaying individual web pages, it presents relationships between entities. Searching for “Leonardo da Vinci” displays not just a biography but also related entities like “Mona Lisa” and “Renaissance.”
Case Study: How Wikipedia and Amazon Dominate with Semantic Structure
- Wikipedia uses semantic linking between articles, creating a massive web of interconnected entities that search engines easily interpret.
- Amazon structures product data semantically, helping Google understand relationships between products, features, and user intent—enhancing visibility in product searches.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Semantic SEO
Keyword Stuffing and Over-Optimization
Repeating the same keyword unnaturally harms readability and ranking. Semantic SEO values context and coherence over raw frequency.
Ignoring User Intent and Context
Publishing content that doesn’t match what users are searching for leads to high bounce rates. Always research and address the why behind the query .
Lack of Topic Authority and Internal Linking
Disorganized content and poor linking confuse search engines. Build a content ecosystem —each article should reinforce your topical expertise.
Future of Semantic SEO and AI in Search
Role of Generative AI in Semantic Understanding
With the rise of AI-driven models like ChatGPT and Gemini , search is becoming more conversational. Generative AI interprets context dynamically, offering nuanced, human-like answers. This trend enhances how users discover and interact with information .
Predictive Search and Personalized Experiences
Future search engines will anticipate user needs before queries are typed. By analyzing browsing patterns, preferences, and context, predictive SEO will deliver hyper-personalized results , making search faster and more intuitive.
FAQs
Conclusion
Semantic SEO represents a fundamental evolution in how search engines understand and deliver information. By interpreting the meaning behind queries rather than simply matching keywords, search engines can offer faster, more relevant, and more intuitive results .
For content creators and marketers, embracing semantic SEO isn’t optional—it’s essential. By structuring your content around intent, entities, and relationships , you not only improve visibility but also contribute to a richer, more satisfying user experience .
As AI continues to redefine search, one truth remains clear: the more you align your content with human understanding, the better you’ll rank—and the happier your users will be.
📧 Stay Updated
Get the latest web development tips and insights delivered to your inbox.

